The cradle of human civilization – Africa is continuously showing economic development for the past few decades. Many nations have emerged as a shining beacon of progress in the African continent.

It won’t be wrong to say that this prosperity and economic development is driven by the increase in the remittance payments in the continent. After all, remittance is the best indicator to show the relationship between migration and development.
As per World Development Indicators 2019 database of 80 developing countries for the period of 1974-2014, an average 1 per cent increase in remittance can raise the GDP of the country by almost 0.07 per cent in the long run.
Another study by Pew Research Remittance shows that 8 out of the 10 fastest-growing populations of expats are nationals of the countries from the sub-Saharan Africa region. This expat population can be one of the major reasons behind the increased cross-border remittance transfers in future years.
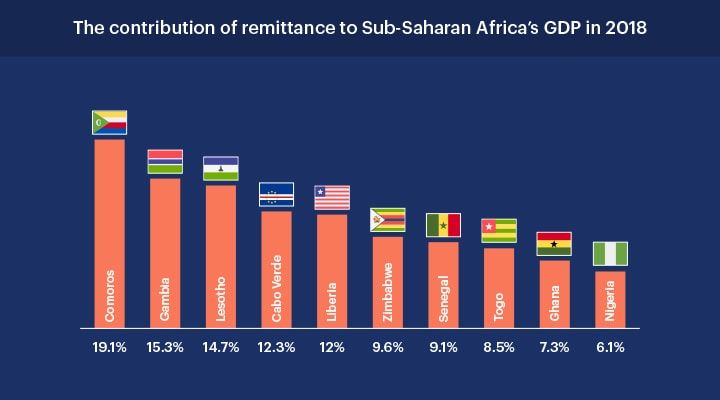
It’s estimated that more than 25 million expats from the sub-Sahara African countries remitted approximately USD 46 billion in 2018. And this trend is expected to continue and grow in 2020.
It won’t wrong to say that Africa is a paradise for the FinTech industry, especially when it comes to the international remittance industry. Factors like a high volume of unbanked population, high penetration of smartphone usage, and increasing migrating population make it the perfect place for digital remittance industry to thrive.
But setting up a remittance business in Africa is not a cakewalk by any stretch of the imagination. There are plenty of hurdles and challenges that one has to go through before setting up their remittance business.
In this blog, we will provide you with everything that you need to know before starting your remittance business in Africa. We will discuss Africa remittance market trends, popular players, rules & regulations in various African countries, challenges, and solution.
Remittance market trends in Africa
African nations are very crucial as they form a massive and ever-growing slice of world’s remittance market. According to the World Bank, in the year 2018, the remittances to the Sub-Saharan region grew by 10% to $46 billion. The major reason behind this upsurge is the steep increase in the African migration which has fuelled the growth of remittance in the continent.
There are many challenges as well as opportunities associated with remittance in Africa. For an instance, Africa has the highest costs in the world averaging around 9% for making a transaction of $200. This cost is quite high when we compare it to the world’s average of 7%.
Although when it comes to infrastructure then Africa has a real advantage. This is mainly because Africa was an early adopter of digital wallets and mobile money technology via M-Pesa in Kenya.
Many other FinTech firms followed the lead of M-Pesa to set up their own remittance services and as a result of which today there’s a rich foundation that supports remittance for the African diaspora.
We are also seeing increased collaboration and partnerships among mobile operators, money transfer operators, FinTech, and banks to maximise the potential of digital technology along with improving remittance infrastructure.
Authorities and policymakers are also encouraging the growing competition in the remittance market so that the full potential of the domestic remittance market can be fully exploited.
The best example of this is of African Development Bank which is working with the African government to introduce various measures and policies that will increase the remittance flows.
The launch of PRIME (Platform for Remittances, Investments and Migrants’ Entrepreneurship in Africa) in January 2019 was one of such many measures. The main objective of PRIME is to cut the costs associated with remittance so that remittance services can be more widely used across the African continent.
Major players of the African remittance industry
The competition among the regional as well as the global remittance service providers has been intense in the African region.
Many prominent mobile telecommunication operators (MTO) and banks such as RIA Financial, WorldRemit, UAE Exchange, Skrill, etc. are making the competition even more healthy and cut-throat by offering online, mobile, point of sale, account, and a combination of these channels to their users.
Let’s have a look at the biggest remittance players of Africa who are shaping the remittance industry in the continent.
Western Union & MoneyGram
Western Union & MoneyGram are two of the biggest money transmitters that have a combined market share of 50% in the three-quarters of SSA countries. Moreover, they have over 90% market share in countries like Angola, Zambia, Malawi, Zimbabwe, and Liberia.
Dahabshill
Dahabshill is the largest African remittance business with branches and agent locations in around 126 countries across the globe. They have 40 years of experience and are known for providing their valuable services in the East Africa region.
VISA
VISA operates the largest retail electronic payment network in the world – Visanet is responsible for linking 2.5 billion Visa cardholders in more than 200 countries. Moreover, it has around 13,700 financial institutions and over 40 million merchants.
Zoona
Zoona is an African startup which helps communities to thrive by enabling its users to send money at crucial times. Zoona has processed more than $1 billion of bill payments, money transfers, and other financial services.
Paytoo
Paytoo signed an agreement with Infenix which enabled them to offer their remittance services to over 79 million users in around 29 African nations.
Mama Money
Mama Money is one of the most dominant money transfer companies who aim to reduce the cost of sending money across borders. First, they have started with Zimbabwe where they want to impose an ambitious flat charge of 5%.
They have also partnered with the Central African Building Society (CABS) in Zimbabwe which is 100% Old Mutual owned subsidiary.
Apart from these, there are other names too such as MTN Mobile Money, Orange Money, WorldRemit, Ria Financials, M-Shwari (Kenya), Homesend Transfer-to, MSF Africa, Equity Bank (Kenya), etc.
Remittance regulations in Africa
Every business irrespective of their industry has some set of rules & regulations under which it functions and remittance business is no exception. Rules & regulations pertaining to the remittance industry are very critical as they shape the innovations in the global remittance industry. This is the reason why they are also called the backbone of international money transfers.
If anyone wants to start money transfer business then they must comply with laws and regulations laid by the local authorities. Now every country has different rules & regulations for international remittance businesses. You must comply with all the laws of the country in which your money transfer business is in operation.
If we talk about Africa, then most countries only permit banks to pay remittances. Banks comprise more than 50 per cent of money transfer businesses.
If anyone wants to start their remittance business in Africa then they must get a license in the originating country. Getting a license is a costly affair. So, if you’re thinking of setting up your remittance business in Africa then you must have a decent amount of money for the compliance process only.
Let’s have a closer look at the regulatory framework of the remittance industry in Africa. The rules and regulations pertaining to international remittance in Africa cover the following regulatory issues:
- Authorized paying institutions
- Significance of non-bank financial institutions
- Requirements for money transfers
- Ownership of foreign currency accounts
- Anti-money laundering
Let’s have a look at them one by one.
Authorized paying institutions
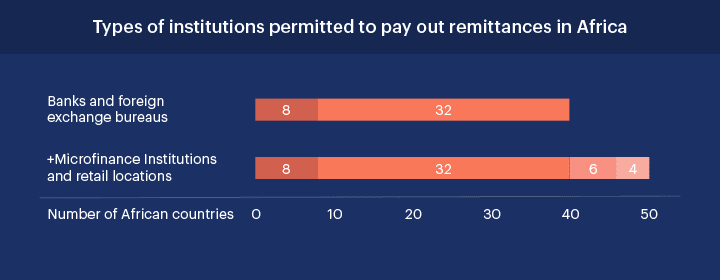
As mentioned earlier, African countries only permit banks and secondary foreign exchange bureaus to make cross-border payments. Out of 50 African countries, eight permits only banks.
Whereas, 32 countries have authorized banks as well as foreign exchange bureaus. There are six countries which also allow MFIs along with foreign exchange bureaus and banks. Retail locations are also permitted to make remittance along with the earlier three options in four African countries.
The role of non-bank financial institutions
Non-bank financial institutions such as MFIs and credit unions play a huge role in expanding the reach and accessibility of remittances. Although in many African nations, they have to go through extreme scrutiny to provide cross-border payments.
As per a study, Kenya, Ghana, and the Democratic Republic of Congo are the only countries which allow MFIs to carry out remittance transfers. Even there, their participation is restricted due to inadequate technical capacity.
Limits on and requirements for money transfers
Regulations regarding restrictions are essential as they protect against frauds and scams. Different countries have different regulations regarding the amount limit that is permitted to make cross-border payment.
For example, countries like Morocco, Botswana, Tunisia, and Burundi has a limit on inbound transfers. All the transfers of the amount under US$10,000 are reported to authorities via banking channels and customs. Also, there are 23 countries where amounts less than US$10,000 are reported to the central bank.
In more than half of the African countries, the proof of beneficiary is compulsory to make the outbound transfer. Zimbabwe and South Africa are the countries where you can only send money to your relatives whose need for money has been proven by the central bank.
Ownership of foreign currency accounts
Remittance recipients can own foreign currency accounts. This ability enables them to receive as well maintain savings from remittances and that too in the foreign currency. Almost half of all African countries allow their residents to start a business foreign currency accounts or an open personal account without any need of permission from the central bank.
Whereas, in nine countries, residents need to get permission from the concerned regulatory body for opening an account. The rest of the countries don’t allow their residents to obtain such accounts either for business or personal use.
All African countries allow non-residents to open foreign currency accounts; however, they need to seek approval from the central bank in UMAC, Franc Zone, and eleven other countries.
Anti-money laundering
Most of the African nations introduced anti-money laundering legislation somewhere around in 2002 in the wake of 9/11 attacks. If we talk about anti-money laundering in regards to remittance transfers, then the compliance is difficult to achieve in an efficient manner since the costs are really high.
Additionally, record-keeping costs, extra compliance staff, and training of employees increase the overall cost of doing business.
Challenges associated with traditional remittance
We have already figured out how complex and challenging remittance payments and services can get. However, that’s not the end of it.
The traditional remittance services that are so prevalent in many African regions have their own set of challenges that makes cross-border payments an inefficient practice. Let’s have a look at them one by one.
Not suitable for unbanked people
In traditional bank-to-bank remittance, both sender and receiver must have a bank account. This is the reason why traditional remittance services are not suitable for those people who don’t have any bank account.
Slow transfer speed
Bank-to-bank transfers in traditional remittance go at a snail’s speed. It can take five days or even more than that for the completion of the transfer. Moreover, the receiving banks can further delay the transaction by holding up the release of funds for 2-4 days. Banks generally hold funds to ensure that the transaction is devoid of any fraudulent activity.
Limited access
Traditional remittance services come with a plethora of restrictions when it comes to the accessibility of these services. For an instance, many exchange banks, agencies, and kiosks have restricted operational hours. Moreover, due to COVID-19 pandemic, these working hours were further restricted.
Secondly, users either sender or receiver has to travel and stand in the queue for sending and receiving funds.
Poor customer experience in COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, traditional remittance services delivered very poor customer experience to the users. Reduced opening hours, no infrastructure for low-touch remittance operations, and uncertainty of transfer were among the biggest discomforts felt by the users.
DigiPay’s remittance solution
As earlier mentioned, the COVID-19 pandemic has rendered the traditional remittance services slow, cumbersome, and inefficient. That’s why there’s a need for a robust digital remittance solution can overcome the challenges posed by COVID-19 pandemic.
All the above-mentioned challenges including the COVID-19 challenge can be overcome with the help of DigiPay’s advanced and next-gen remittance solution. DigiPay’s remittance payment solution comes with state-of-the-art technology and cutting-edge features which make cross-border payments easier than ever.
Not only this, but DigiPay’s cross-border payment solution also supports various transfer methods used in different countries. This is what makes DigiPay a truly global remittance solution. Let’s have a look at these different remittance payment methods in details.
Mobile-to-Mobile transfer (M2M)
Customers can send money to their friends and loved ones directly from their smartphone. Similarly, the receivers can also receive the remittance amount directly into their accounts. This amount can be later used for future financial transactions.
In this case, the sender’s account is debited and the receiver’s account is credited with the transaction amount along with the applicable charges.
Read More: DigiPay’s next-gen mobile money solution.
Mobile-to-Bank transfer
In this scenario, customers send money to their family and friends directly from their phones and the receiver receives the remittance amount directly into their bank account. This can be achieved either by a third party switch that enables international transfers or via direct API integration of the receiver’s bank.
Mobile-to-Cash transfer (M2C)
In this scenario, customers can send money to their family member and friends from their smartphone and the receiver will receive the amount via their International Money Transfer (IMT) partner agent.
In this case, the sender’s account is debited and the receiver receives an SMS notification so that he knows when to go to his IMT partner for collecting the money. Once collected, the sender receives a confirmation SMS.
Advanced features of DigiPay’s remittance solution
As we mentioned earlier, DigiPay’s cross-border payment solution stands out among other remittance solutions due to its advanced features. These features enable users to make cross-border money transfers with extreme ease, convenience, and speed. Let’s have a look at these features one by one.
Lightning-fast fund transfer
With DigiPay’s remittance solution, users can enjoy lightning-fast fund transfers. Users can send money to their loved ones across the border within a day.
Limit orders
Users can set the exchange rate of their preference in such a way that the transfer takes place only when that particular rate is achieved.
Easy-to-use
DigiPay’s easy-to-use remittance payment solution uncomplicates the entire remittance procedure. It enables users to transfer money with the utmost ease.
Track payment status
With DigiPay’s remittance solution in place, users can track the status of their remittance transfer via email updates, push notifications, SMS, etc.
Forward Contract
With the help of forward contract, admin can enable customers to lock the exchange rate for their future transactions.
Multi-party settlements
DigiPay’s remittance solution provides automatically generated multi-party settlements and reconciliation files.
Transfer limit
DigiPay’s remittance solution enables admin to set maximum as well as minimum transfer limits for customers.
Exchange rates
Admin can set dynamic and set exchange rates for the customers through XE.com, Google Finance, Yahoo, etc.
Conclusion
The remittance industry in Africa is prospering with each passing day. The continent has all the factors that work in favour of digital remittance service providers.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has made life difficult for the traditional remittance service providers and their users. This further makes the case for a digital remittance solution stronger.
If you’re a FinTech entrepreneur then there can’t be a better time to start your remittance business in Africa. In this blog, we have already provided you with all the important information, insights, and tips to start your remittance business in Africa.
Furthermore, you can gain the first-mover advantage by setting-up your remittance business powered by DigiPay’s ready-made remittance payment solution. So, what are you waiting for? Get DigiPay’s next-gen remittance solution now.