Even before the pandemic struck, the payment industry was quite dynamic over the past few years. Double-digit growth rates, dizzy valuations, and technological advancements at an unprecedented rate are some of the indicators that prove it. However, one must not underestimate the small volume decline due to COVID-19.

The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the payment industry has been less severe as compared to the other sectors of FinTech. However, it doesn’t mean that the payment sector is completely immune to the COVID-19 effects.
With social distancing and lockdown in place, the travel and transport industry has seen a tremendous decline. This decline has also affected all the payment service providers who were associated with the travel industry.
Also, the economic uncertainty due to the pandemic has forced people to spend money very cautiously which has resulted in the overall reduction of consumer spending. This reduction in consumer spending affects both the payment processing services as well as to those card issuers who get their revenues from the interchange fees.
As per McKinsey, the global payment revenues are expected to decrease by 10 per cent which would amount to 1.86 trillion US dollars in case of a muted recovery scenario. This is huge as the Pre-COVID-19 estimation for 2020 predicated the global payments revenues to reach around 2.17 trillion US dollars.
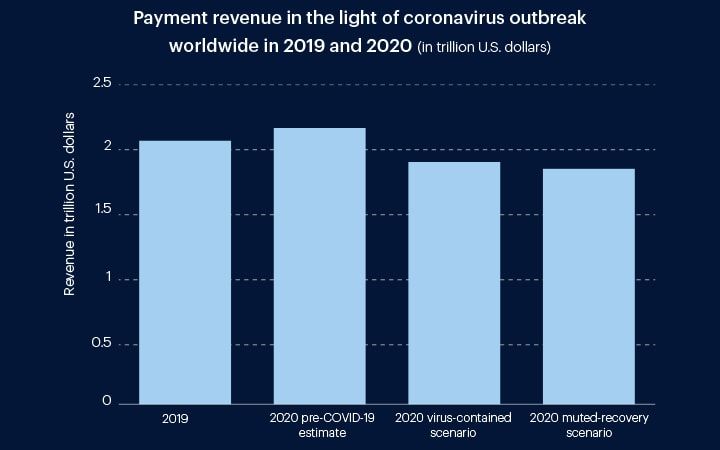
The pandemic has also caused people to follow social distancing norms along with reducing physical contact among various members of their own household. This has also caused to reduce the use of cash in many parts of the world.
These are just a few of the examples, the COVID-19 pandemic has completely transformed the shopping behaviour which has pushed merchants on the verge of bankruptcy. This situation is here to stay for longer than we are anticipating now. And it might have wide-reaching implications on the payment industry as a whole.
In this article, we will try to discuss the impact on COVID-19 on the payment industry in great detail. We will have a look at its impact on several sectors one by one.
Mobile money
According to research released by MX, which is a digital transformation platform for credit unions and banks, shows that there’s a rise of 50% in the mobile banking engagement since the end of 2019. It also showed that the payments made via debit and credit cards saw a decline of 25% during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Interestingly 60% of participants also said that their prime financial institution fails to make them financially stronger. And they would prefer to move to mobile banking.
According to the study by payment firm FIS, the COVID-19 pandemic is also driving the consumers in the US towards digital payments and mobile banking.
According to the study, around 45% of the banked participants have changed the way they interact with their financial institutions. 39% of Gen Xers, 46% of baby boomers, and 36% of millennials are now using online or mobile banking.
The study also shows that around 31% of participants would prefer to use mobile payments and contactless payment methods instead of cash due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
This surge is not only limited to the US. Even in a developing country like Rwanda, there is mass adoption of mobile money services in the wake of COVID-19 pandemic. There has been a sudden increase in the person-to-person (P2P) transfers in the country.
To get a better perspective let’s compare this with the first week of January when the total amount of fund sent via P2P transfers was around RWF 7.2 billion which is equivalent to the US $7.6 million. However, in the last week of April, this value increased to RWF 40 billion which is equivalent to over US $42 million. The increase is roughly over a mammoth 450%.
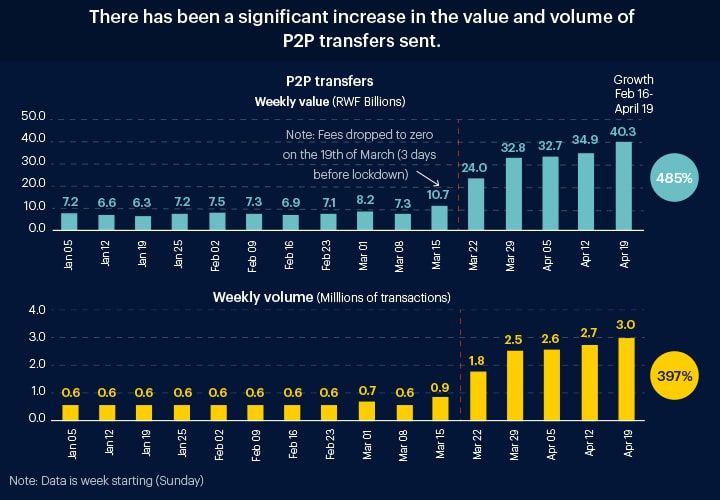
The story of Nigeria is also quite similar. The mobile money transactions in the country grew by 15% in the month of March and many experts believe that the percentage would rise in the coming days.
Not only consumers but also governments and authorities have leveraged mobile money to offer efficient and affordable financial services along with addressing the practical challenges. Mobile money has emerged as an effective and social-distancing friendly way to avoid cash.
Mobile money and other digital payment options such as contactless payments, mobile wallet payments, QR code payments, NFC payments, facial recognition, etc. can inhibit the spread of the virus.
Card-based payments
Card payments have witnessed a surge of 75% during the COVID-19 pandemic. As per the new data by PayPoint, this surge is due to fear that consumers have over handling cash. As per the trading update, the card payments saw a surge of 75.3% and 74.4% for year-on-year during the period from 1st to 17th April and from 18th April to 17th May respectively.
The same period also saw a drop in the ATM transactions by around 39.9% and 33.31% respectively. The main reason behind this drop was of customer’s reluctance to handle cash. Also, many customers preferred to stay indoors due to the pandemic.
COVID-19 acted as a catalyst for a trend that was already taking place before the pandemic. Before the pandemic, card payments grew by 20.6% by in last one year till 31st March 2020. Whereas, the ATM transactions dipped by 4.1% during the same period.
One other reason behind the fall of ATM transactions was of UK government’s lockdown in 23rd March which shut down all the non-essential retail stores.
The COVID-19 pandemic has instilled a fear in everyone’s mind regarding cash handling. Everyone is avoiding the use of cash during the pandemic. According to the payment pundits, the COVID-19 situation is here to stay for a long time.
People will slowly adjust in the new normal by adopting card and cashless payments over cash. Even the convenience stores are adapting their offering to ensure that every customer can easily use their credit and debit cards for making seamless and safe payments.
International remittances
International remittances have been severely hit by the COVID-19 pandemic. Global remittances are estimated to decline by 20 per cent in 2020 as a result of the crisis caused by the pandemic. This decline is considered as the sharpest one in the recent past. The main reason behind this decline is the fall in wages of migrant workers.
This is an alarming situation as around 75% of the all world’s migrants work in the countries where almost three-quarters of global COVID-19 cases have been reported. Moreover, the remittances sent by migrants in these countries is as high as 90%.
These workers are amongst the sections who are vulnerable to the loss of employment during a situation of the economic crisis in the host country. If we have a look at the remittances of low and middle-income countries (LMICs) then the estimated decline is about 19.7 per cent to $445 billion. This decline is a major chunk of many vulnerable households’ financing life.
Remittances have played a crucial role in uplifting poverty in millions of lower and middle-class families in developing countries. They have enhanced their nutritional income. The remittance fund is also associated with increased spending on education and reducing the practices of child labour.
Read More: Cross border payments made easy with DigiPay
A sudden fall in the remittances will certainly have an adverse effect on these families as it will shift their spending from the above-mentioned areas to resolve immediate livelihood needs and food shortages.
According to David Malpass, Group President of World Bank, “Remittances are a vital source of income for developing countries. The ongoing economic recession caused by COVID-19 is taking a severe toll on the ability to send money home and makes it all the more vital that we shorten the time to recovery for advanced economies,”.
“Remittances help families afford food, healthcare, and basic needs. As the World Bank Group implements fast, broad action to support countries, we are working to keep remittance channels open and safeguard the poorest communities’ access to these most basic needs.” He added.
Apart from the migrant workers and their families, remittance service providers have also been severely impacted by the current pandemic. Managing liquidity becomes difficult for remittance service providers when there are volatile exchange rates and unexpected flows. Remote working along with forced closures also directly affects the service provider’s ability to continue its operations.
Remittance service providers are struggling to onboard their clients on digital channels due to obligations on face-to-face customer verification and lack of digital infrastructure in the market.
Moreover, factors like adequate financial awareness, lack of identification documents, digital literacy, and access to digital technology among migrants and their families mean that there can be increased dependability and reliance on the informal remittance channels when the formal channel decline.
Increased rates of digital financial inclusion can prove to be an effective way to mitigate this as well as in continuing the flows in the formal channels.
Customer loyalty and rewards
COVID-19 played a major role in changing and reshaping the customer’s shopping behaviour. When the pandemic struck the US, a large number of consumers started to stockpile products. The stockpiling was to such an extent that Amazon had to notify their customers in March that they were out of stocks for certain household staples.
In their statement, Amazon said “working around the clock with our selling partners to ensure availability on all of our products, and bring on the additional capacity to deliver all of your order.”
Events like these are compelling shoppers to seek alternative brands. According to a report by McKinsey, more than 75% of the consumers have tried new places to shop, new brands, and new methods of shopping during the pandemic.
The major factor which caused a transition in customer’s shopping behaviour was product availability followed by the other two factors like promotions and better prices.
Read More: Boost your profit with digipay’s Customer loyalty and reward solution.
According to a report by Wharton School’s Baker Retailing Center and WisePlum “Not all problems are created equal in their impact on customer loyalty. In fact, the top 10 most frequent problems were different from the topmost damaging problems,” the study stated.
It means that the most frequent problems that were experienced by the users were not necessarily the most damaging to the customer’ loyalty. If we look at the most damaging problems it includes:
- Return processes
- Difficulty in navigation in-app or website
However, the most frequent problem was around the availability of products as per the report.
COVID-19 pandemic has brought a unique situation in front of all the retailers. They quickly need to find out an effective way to maintain and enhance their customer loyalty. Quick adoption of the digital customer loyalty approach is a foolproof way to ensure customer loyalty.
Retailers can use mobile wallet solutions and services which comes with a robust customer loyalty program. This module helps them to offer personalized rewards and loyalty points that skyrocket their profits by retaining, engaging, and adding new customers. With efficient rewards and loyalty solution in place, they can:
- Enhance profitability
- Maintain seamless communication
- Collect and access vital information
- Increase demand
Read More: Cash in with customer loyalty programs on mobile wallets.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has widely impacted the payment industry as a whole. Few of the sectors have been impacted positively, whereas, the rest have faced its adverse effects.
After discussing the impact of COVID-19 in all the payments sectors, one thing is pretty clear that if any business wants to survive in the pandemic, then they must adopt digital payments methods. They must offer their consumers a simple, convenient, and social-distancing friendly mode of option.
If you’re such business or an enterprise who is looking to adopt cutting-edge digital payment methods then choose DigiPay which is a cutting-edge mobile money and mobile wallet solution that comes with all the important modules such as international remittance, customer loyalty, merchant services, and many more.