Over the past decade, East Africa has seen a significant shift in the way people access and use financial services. The region has experienced a rapid increase in financial inclusion, thanks to the emergence of digital financial solutions.
These digital solutions have enabled individuals and businesses to access banking services that were previously out of reach, helping to drive economic growth and development.
According to a 2022 study by Statista, in 2021, formal financial services and products were accessible to almost 84 percent of households in Kenya. This marked a significant improvement from 2006 when only around 57 percent of households had access to financial services in this East African country.
Other East African countries like Tanzania and Uganda have also been highlighted by the Word Bank in their Global Findex Database 2021 showing a significant increase in financial inclusion in these countries.
The above statistic indicates that East Africa has been gradually moving towards financial inclusion which will ultimately help them boost their economy as a whole.
In this blog, we will explore the evolution of financial inclusion in East Africa, highlighting the state of financial Inclusion before digitalization, the rise of digital financial services after digitalization, the impact of digital finance on financial inclusion in East Africa, and what the future holds for East Africa.
The State of Financial Inclusion in East Africa Before Digitalization
Financial inclusion has been a critical challenge in East Africa for a long time. The majority of people in the region have been excluded from the formal financial sector, which has impeded economic growth and social development.
However, the rise of digital technologies has revolutionized the financial sector, making it easier and cheaper to provide financial services to people who were previously excluded.
Here are some key points on the state of financial inclusion in East Africa before digitalization:
Limited Access to Formal Financial Services
Access to formal financial services was limited to a small percentage of the population in East Africa. Banks and other financial institutions were concentrated in urban areas, leaving people in rural areas with limited access to financial services.
Low Penetration of Mobile Phones
Before the advent of mobile money services, mobile phone penetration was low in East Africa. This made it difficult to provide financial services to people who lived in remote areas where banks and other financial institutions were not present.
High Levels of Informal Financial Services
People in East Africa relied heavily on informal financial services, such as savings groups and money lenders, to meet their financial needs. However, these services were often unregulated and exposed people to high levels of risk.
Limited Financial Literacy
Many people in East Africa lacked the financial literacy needed to make informed decisions about financial products and services. This made it difficult for them to take advantage of formal financial services when they were available.
Limited Financial Infrastructure
The financial infrastructure in East Africa was underdeveloped, with limited payment systems and a lack of interoperability between financial institutions. This made it difficult to provide financial services to people who lived in remote areas.
To get a more clear picture of the state of financial inclusion in East Africa before digitalization let's have a look at the timeline of the same in the table below.
| Time Period | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Pre-2000s | Limited access to formal financial services, banks, and financial institutions concentrated in urban areas, people in rural areas with limited access to financial services, low mobile phone penetration |
| 2000s | High levels of informal financial services, reliance on savings groups and money lenders, limited financial literacy, underdeveloped financial infrastructure, limited payment systems and lack of interoperability between financial institutions |
| Late 2000s to Early 2010s | Introduction of mobile money services, the rapid growth of mobile phone penetration, increased access to financial services, the rise of mobile money agents, increased financial literacy |
| 2010s to Present | Continued growth of mobile money services, expansion of financial inclusion beyond mobile money, the introduction of digital banking and other financial technologies, increased competition in the financial sector, increased access to formal financial services |
It is pretty clear and obvious that east africa before digitalization faced a lot of challenges and difficulties in accessing financial services and in moving towards financial inclusion. But digitization changed the entire scenario for East Africa.
The Rise of Digital Financial Services in East Africa Post Digitalization
In recent years, digital financial services have witnessed unprecedented growth in East Africa. The region has become a hub of innovative financial solutions that are transforming the way people save, borrow, and invest money. The advent of digitalization has created a level playing field for entrepreneurs and individuals, leading to a surge in financial inclusion.
Here are some key points that highlight the rise of digital financial services in East Africa:
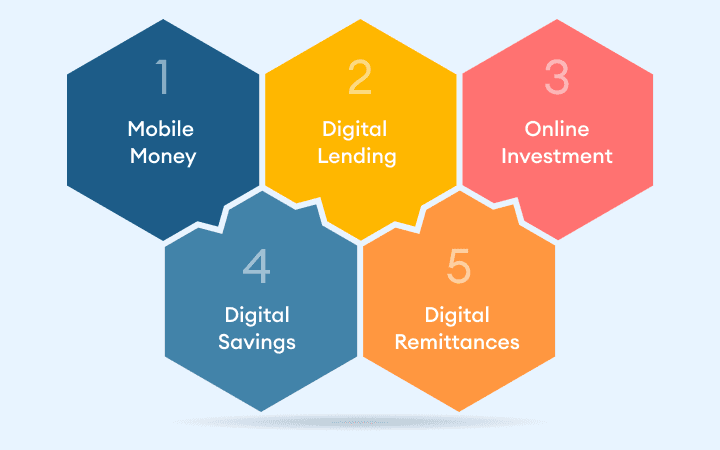
Mobile Money
East Africa is known for pioneering mobile money services, which allow individuals to send and receive money through their mobile phones. And mobile money is one of the key components of digital financial inclusion. M-Pesa, a mobile money platform launched in Kenya in 2007, has been a game-changer in the region.
It has over 40 million active users in Kenya, Tanzania, and other East African countries. Mobile money services have shown a successful graph in fintech while enabling people to access financial services in remote areas and have facilitated small business transactions.
Read more: Mobile Money and Fintech Sucess Stories of Africa
Digital Lending
With the increase in mobile phone usage, digital lending platforms have become popular in East Africa. Companies like Tala, Branch, and PesaZone provide small loans to individuals and small businesses.
These loans are usually disbursed and repaid through mobile money platforms, making them accessible to people without a traditional banking history.
Online Investment
Investment opportunities have also gone digital in East Africa. Platforms like FarmDrive enable farmers to access financing and insurance, helping them to increase their yields and income.
Meanwhile, Abacus, a startup in Uganda, offers an online platform for stock trading, making it easier for individuals to invest in the stock market.
Digital Savings
Traditional savings accounts have been replaced by digital savings platforms in East Africa. Platforms like M-Shwari in Kenya and Tigo Pesa in Tanzania allow individuals to save money and earn interest through their mobile phones.
These platforms also offer micro-insurance products, providing financial protection to individuals and their families.
Digital Remittances
The rise of digital financial services has also made it easier for people to send and receive money across borders. Companies like WorldRemit and Sendwave provide affordable and efficient remittance services to East African countries. This has enabled families to access funds from abroad and has boosted the region's economy.
How have digital financial services become a boon for East Africa?
Financial Inclusion
Digital financial services have played a crucial role in increasing financial inclusion in East Africa. For many people, traditional banking services are not accessible due to high fees, lack of physical infrastructure, or geographic barriers.
Digital financial services, such as mobile money and digital lending platforms, have provided millions of people with access to financial services for the first time.
Increased Efficiency
Digital financial services have made financial transactions faster and more efficient, saving time and money for users. For example, traditional bank transfers can take several days to complete, while mobile money transfers can be completed instantly.
Digital lending platforms like Tala and Branch can disburse loans within minutes, enabling individuals and small businesses to access funds quickly and easily.
Cost-Effective
Digital financial services are often more cost-effective than traditional banking services. For example, mobile money transfer fees are often lower than bank transfer fees, making it easier and more affordable for people to send and receive money.
Digital lending platforms also offer lower interest rates than traditional lenders, making it more accessible for low-income individuals and small businesses to access credit.
Improved Financial Literacy
Digital financial services have also led to an increase in financial literacy. Many digital financial services offer financial education to their users, helping them to make informed financial decisions.
One of the examples of digital financial services depicting improved financial literacy is M-Shwari in Kenya offers financial education and coaching to its users, helping them to understand how to manage their finances better.
Accessibility
Digital financial services are accessible to people who live in remote areas, where traditional banking services are often unavailable.
For example, mobile money services like M-Pesa have enabled people living in rural areas to access financial services easily and conveniently. This has helped to bridge the gap between urban and rural populations in terms of access to financial services.
Better Risk Management
Digital financial services can also help individuals and small businesses manage their financial risks better. For example, digital insurance platforms like Pula in Kenya and BimaAfya in Tanzania offer affordable insurance products to low-income individuals and small businesses.
Access to such platforms provides financial protection against unexpected events. This helps to mitigate financial risk and improve financial resilience.
The Impact of Digital Financial Services on Financial Inclusion in East Africa
Financial inclusion is crucial for economic growth and poverty reduction, and digital financial services have played a vital role in increasing digital financial inclusion in East Africa.
Here are some key ways that digital financial services have impacted financial inclusion in the region, with catchy and informative headings for each point:
Bridging the Banking Gap between services and the unbanked
Digital financial services have bridged the gap between traditional banking services and unbanked populations in East Africa. Many people living in rural areas or low-income households have limited access to physical banks.
But digital financial services like mobile money and digital banking platforms have enabled them to access financial services easily and conveniently.
Increasing Access to Credit for individuals and small businesses
Digital lending platforms have made it easier for individuals and small businesses to access credit. In many cases, people who were previously unable to access credit due to a lack of collateral or credit history are now able to obtain loans through digital lending platforms, providing them with the funds they need to grow their businesses or improve their livelihoods.
Lowering Transaction Costs, Increased Affordability
Digital financial services have also lowered transaction costs, making it more affordable for people to access financial services. Traditional banking services often charge high fees for basic transactions like money transfers
But digital financial services like mobile money transfers are often much cheaper, making it easier for people to access and use financial services.
Empowering Women, Promoting Independence
Digital financial services have particularly empowered women in East Africa, many of whom face significant barriers to accessing financial services. This has helped in advancing women's digital financial inclusion.
Mobile money platforms have enabled women to open their mobile money accounts and take control of their finances, providing them with greater financial independence and opportunities to grow their businesses.
Driving Economic Growth and Prosperity
Digital financial services have the potential to drive economic growth in East Africa by providing individuals and small businesses with the financial tools they need to grow and invest in their communities.
By increasing access to credit and lowering transaction costs, digital financial services can help to spur entrepreneurship and job creation, ultimately leading to greater economic prosperity in the region.
What the Future of Financial Inclusion in East Africa Holds?
As digital financial services continue to expand in East Africa, more people are gaining access to banking services and financial products.
This is having a positive impact on financial inclusion in the region, and several trends and developments suggest the future will be even brighter.
Here is what the future holds for financial inclusion in East Africa:
Continuous Growth and Expansion of Financial Services
The expansion of digital financial services is expected to continue, making it easier for people to access financial services and conduct transactions. This is especially important for people living in rural areas who may not have easy access to traditional banks.
More integrations of fintech and banks to innovate
There will be greater integration between fintech companies and traditional banks, which will lead to the development of new financial products and services tailored to the needs of unbanked populations. This could include microfinance products and services designed for small businesses.
Boost in Digital lending
Digital lending platforms are also expected to expand, providing more people with access to credit. New credit scoring models that take into account alternative data sources will make it easier for people with limited credit histories to access loans.
A win-win! Government with the private sector will promote financial inclusion
Increased collaboration between governments and the private sector is expected to promote financial inclusion in the region. This could involve initiatives like regulatory sandboxes that allow fintech companies to test new products and digital fintech solutions in a controlled environment.
The rise in financial education - Encouraging better utilization of financial services
There will be a greater emphasis on financial education to encourage more people to take various advantages of digital financial services and improve their financial well-being. This is especially important for people who may be hesitant to use digital financial services due to a lack of knowledge or understanding.
Wrap Up
There has been a significant shift in financial services in East Africa from pre-digitalization to post-digitalization. With new and better financial services like mobile money, and lending, investments, savings, remittances all made possible in digital form, the challenges in financial inclusion have been blurred gradually.
With continuous efforts in making financial services more accessible to the unbanked and marginalized population of East Africa, fintech, banks and financial institutions can boost financial inclusion, financial literacy, independence and strengthen the overall economy of the East African countries.
DigiPay.Guru strives to empower banks, financial institutions and fintech companies to make banking and financial services available anywhere to their customers and expand their base quickly along with the most reliable agency banking solution.




